

【Device Papers】Zn-doped Ga₂O₃ based two-terminal artificial synapses for neuromorphic computing applications
日期:2025-09-26阅读:198
Researchers from the Fuzhou University have published a dissertation titled "Zn-doped Ga2O3 based two-terminal artificial synapses for neuromorphic computing applications" in Science China Materials.
Abstract
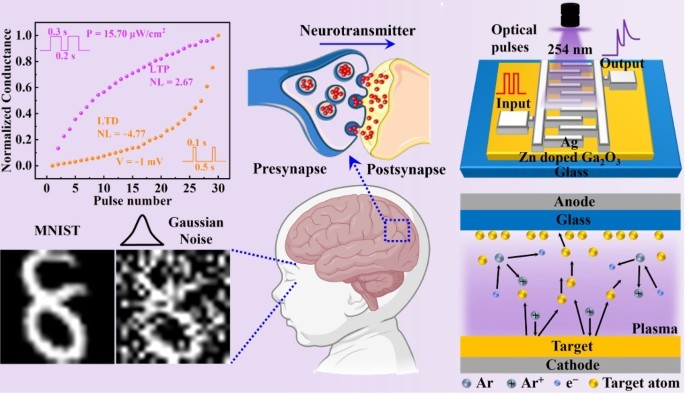
Amorphous gallium oxide (a-Ga2O3) has a low carrier concentration and limited mobility, which constrains its application in neuromorphic computing. In this study, Zn-doped Ga2O3 (ZGO) artificial synaptic devices were fabricated under oxygen-free conditions using radio-frequency magnetron sputtering (RFMS). Compared to undoped Ga2O3, the ZGO device exhibited a 106-fold increase in excitatory postsynaptic current under 254 nm illumination, with the response intensity positively correlated with the optical pulse parameters. Under light pulse modulation, the devices demonstrated dynamic behavior transitioning from short-term plasticity to long-term plasticity, including paired-pulse facilitation and the learning-forgetting-relearning process. Furthermore, the electrical and optical energy consumption of synaptic events are as low as 28 fJ and 2 nJ, respectively. The mechanism analysis indicates that the persistent photoconductivity effect in the ZGO thin film is attributed to the abundant oxygen vacancies. A multi-layer perceptron simulation based on ZGO devices achieved a 90.74% accuracy in handwritten digit recognition, and maintained 76.18% accuracy even with 50% noise. Zn doping provides a new material design approach for Ga2O3-based neuromorphic devices, demonstrating potential for future applications in neuromorphic computing.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-025-3498-5


