【International Papers】SnO₂:F/β-Ga₂O₃ thin-film heterojunctions as sensitive photodetectors for short-wavelength UV radiation
日期:2025-08-14阅读:255
Researchers from the Sharif University of Technology have published a dissertation titled "SnO2:F/β-Ga2O3 thin-film heterojunctions as sensitive photodetectors for short-wavelength UV radiation" in Results in Physics.
Background
The photodetectors are commonly based on the semi-conductive materials, and consist of double thin film thin films and conductive electrical contacts. Gallium oxide (β-Ga2O3) is a wide-bandgap semiconductor that has garnered significant interest for various applications in electronics and optoelectronics due to its unique properties. Gallium oxide has a band gap of approximately 4.5 to 4.9 eV, depending on its crystalline phase. The most stable phase is the beta (β) phase, which is commonly studied and utilized in applications. Its large band gap also enables it to be transparent to visible light, which is advantageous for UV photodetectors. β-Ga2O3 has a high critical electric field (around MV/cm), which allows devices made from this material to handle high voltages without breakdown.
Abstract
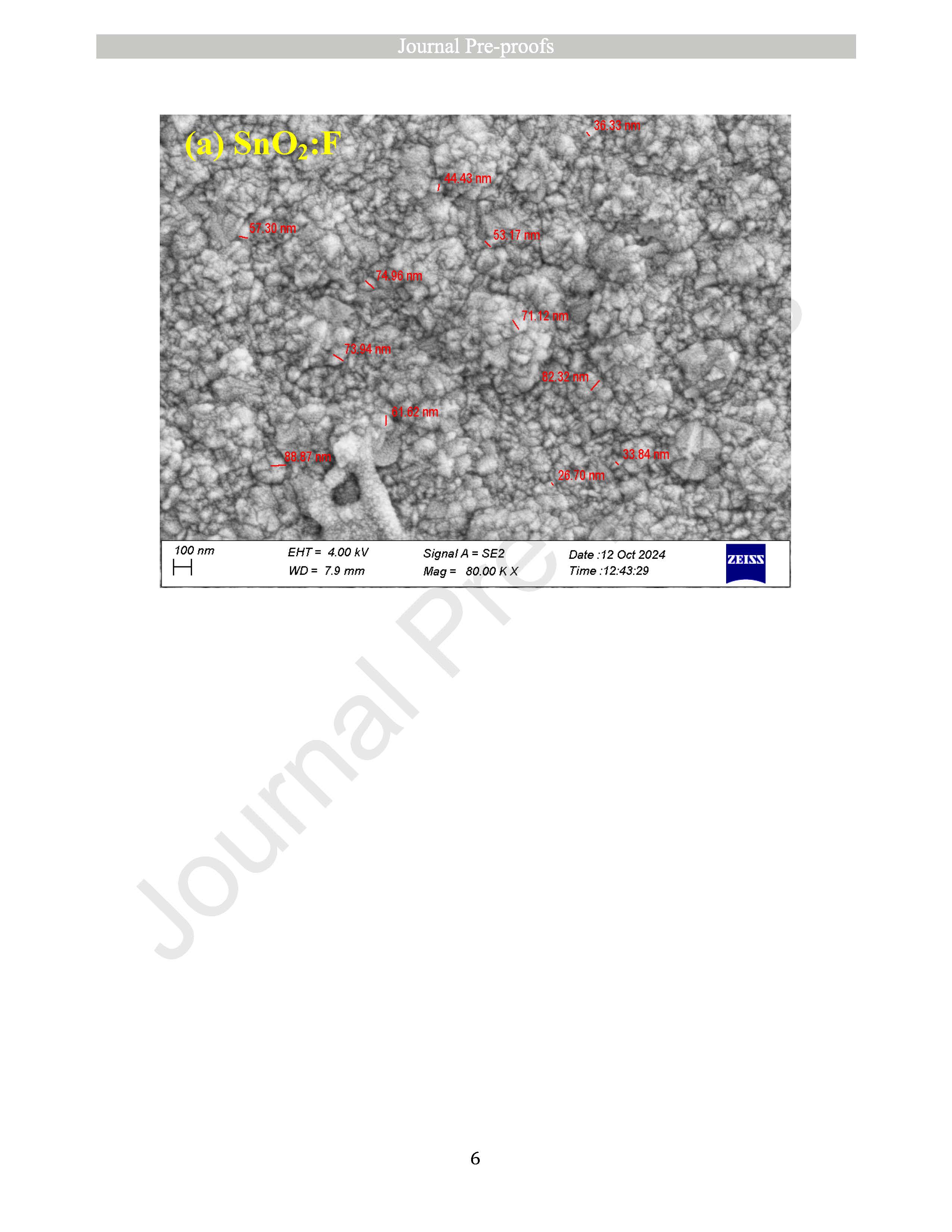
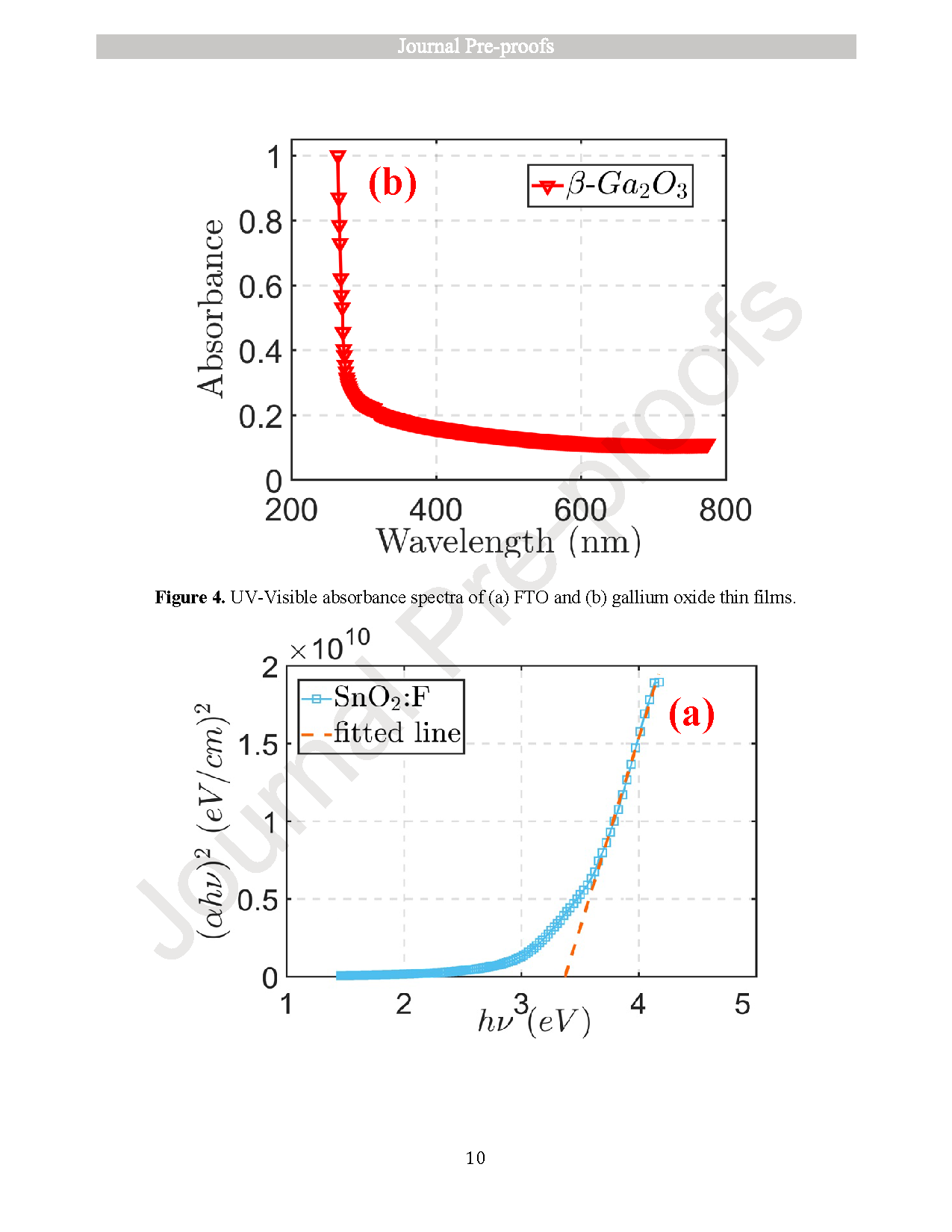
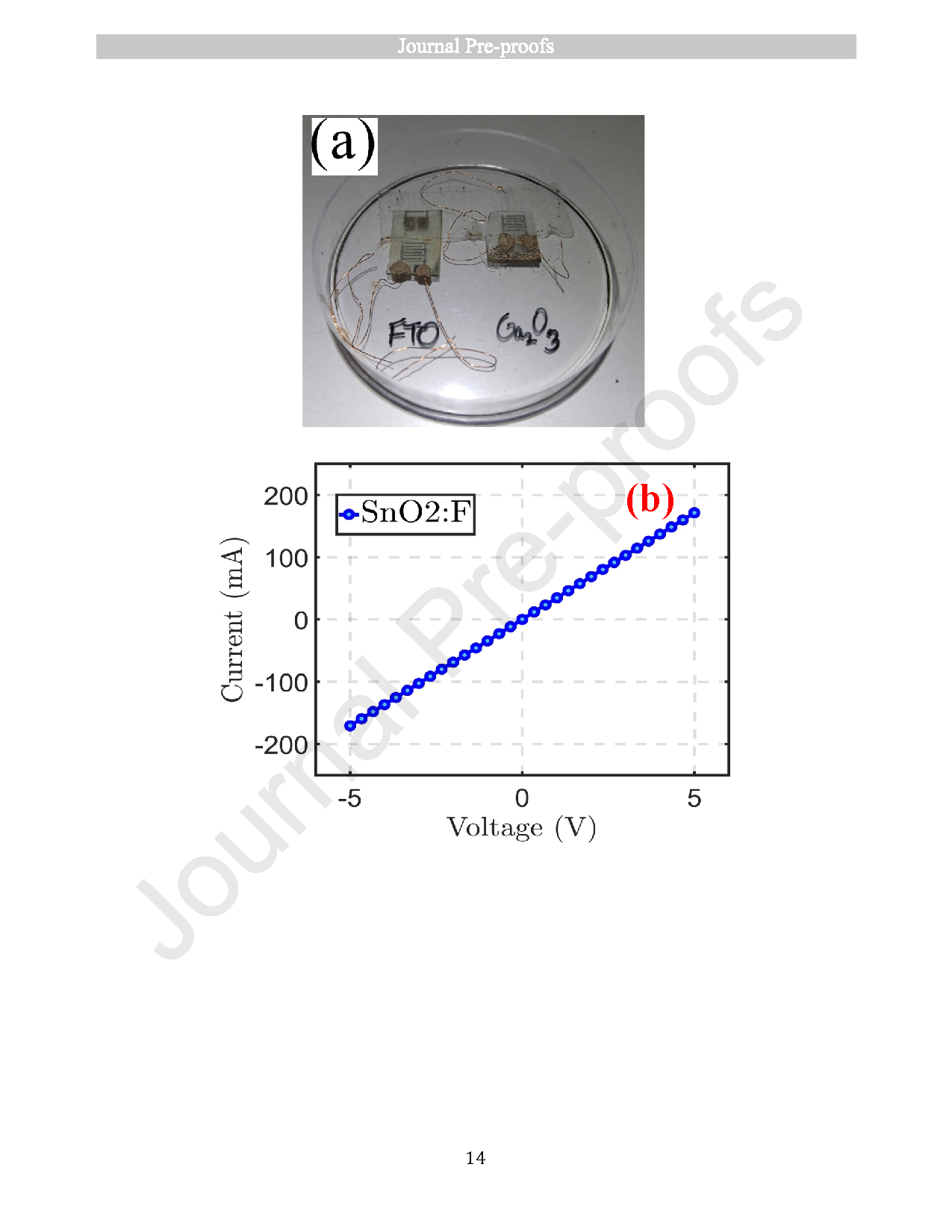
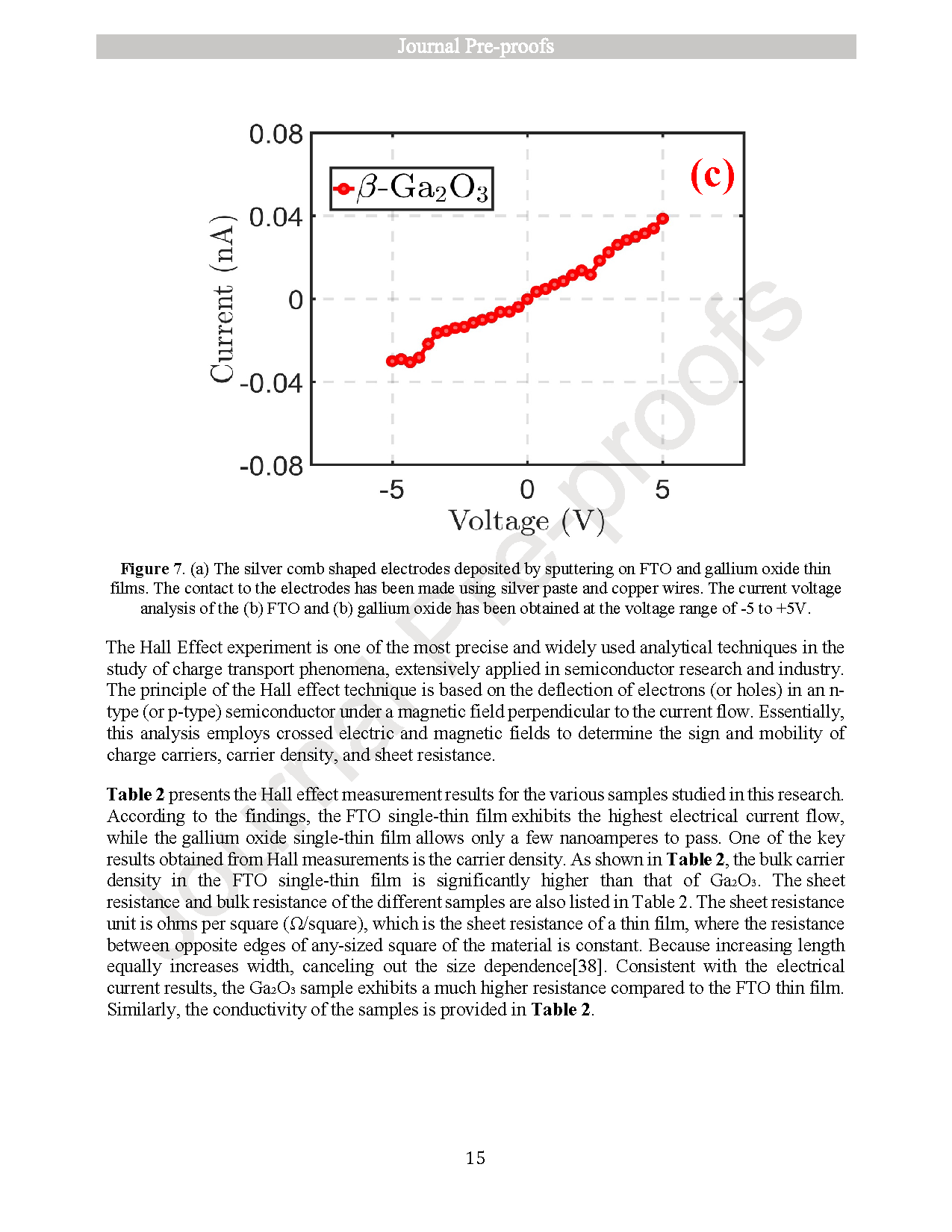
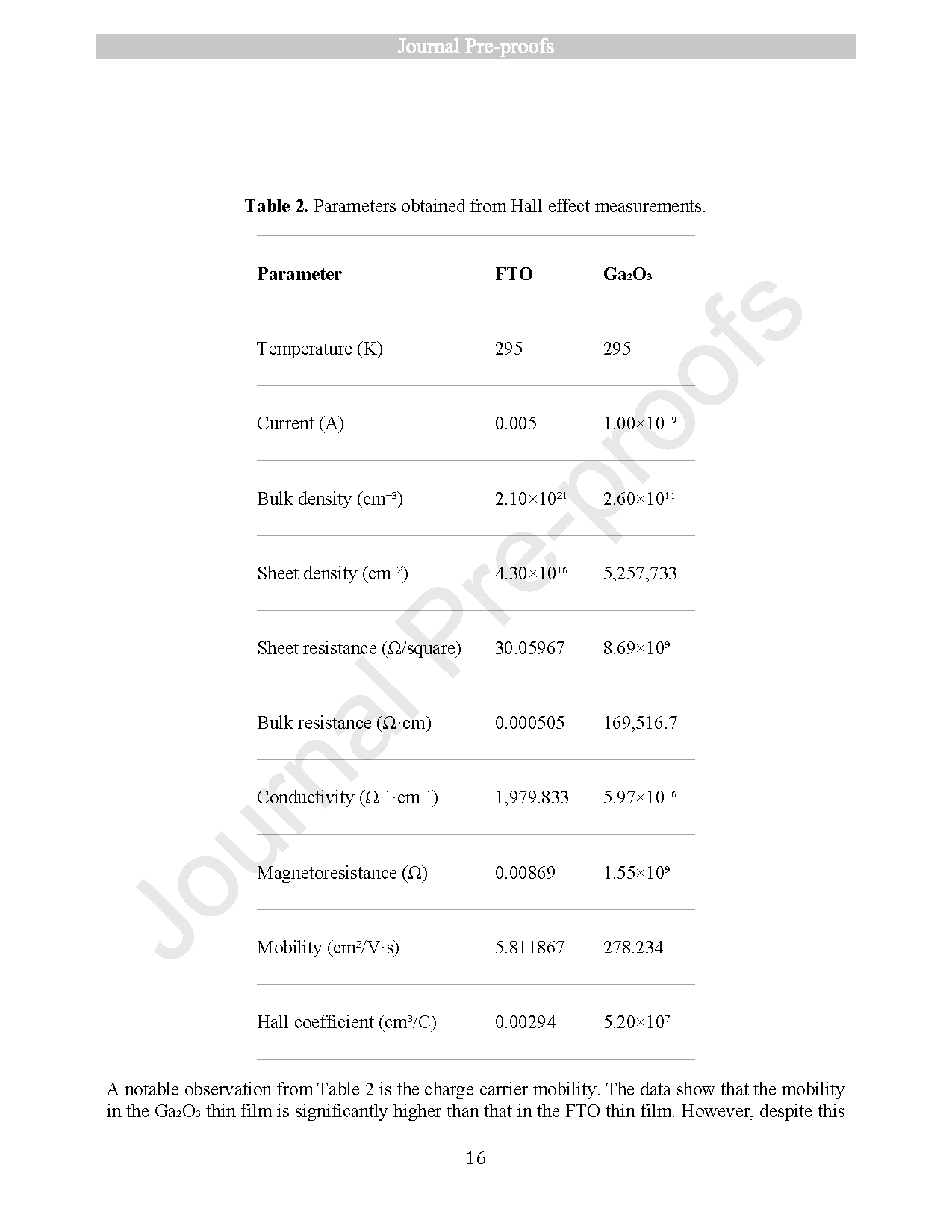
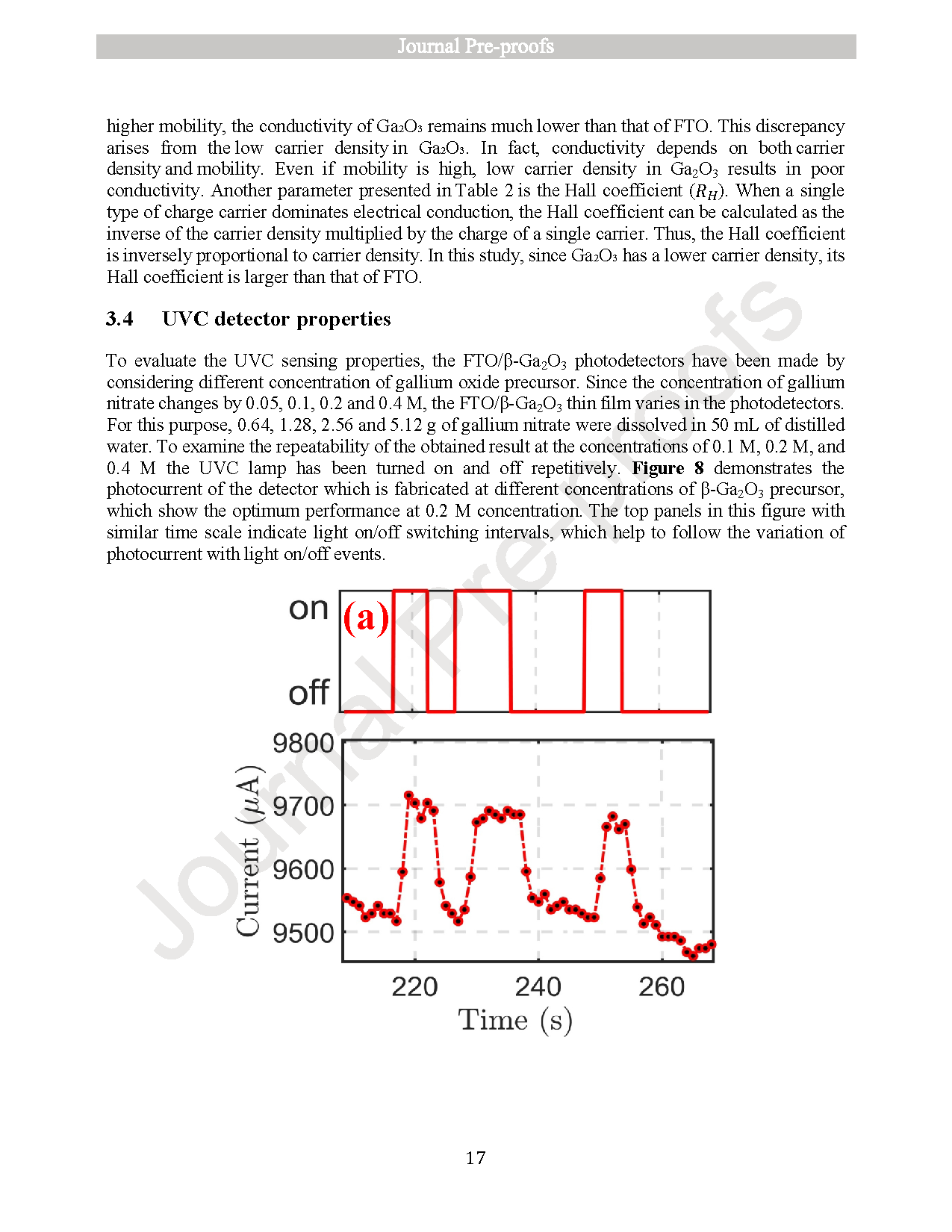
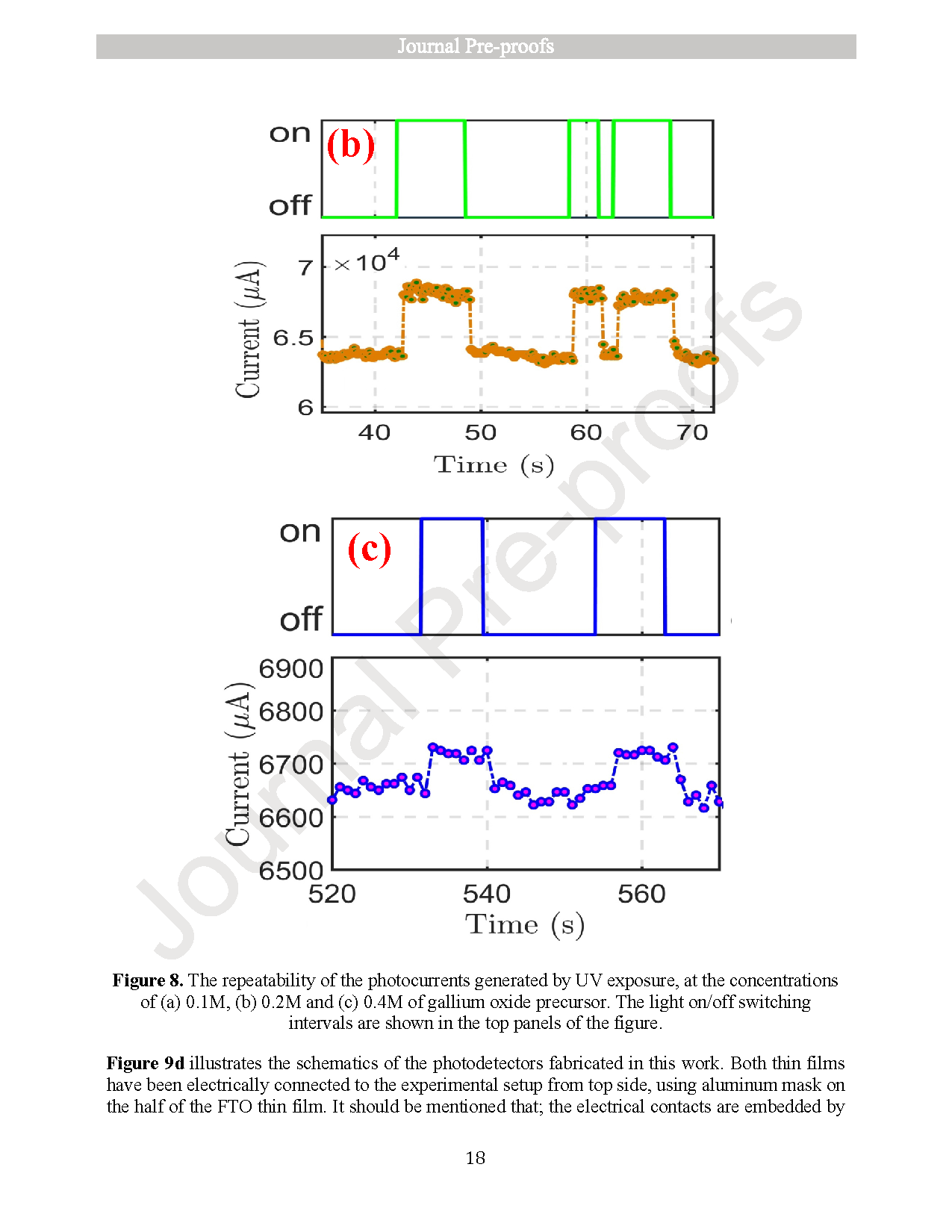
Monitoring UVC radiation from the ozone hole is crucial due to its harmful effects on both the environment and human health. To address this need, photodetectors operating in the short-wavelength ultraviolet (UVC) region are essential. In this study, optical photodetectors based on thin films of fluorine-doped tin oxide (SnO2:F or FTO) and gallium oxide (β-Ga2O3) were fabricated using the spray pyrolysis technique. Initially, individual thin films of SnO2:F and β-Ga2O3 were prepared and characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), UV–Vis spectroscopy, and current–voltage (I–V) measurements. Subsequently, photodetectors composed of stacked SnO2:F/β-Ga2O3 thin films were fabricated, and their photoresponse was evaluated by varying the concentration of Ga2O3. Among the tested concentrations, the device with 0.2 M Ga2O3 exhibited the best performance, with a sensitivity of 6.62 × 10−2, an external quantum efficiency (EQE) of 233.92 %, and a responsivity of 47.72 mA/W. These results suggest that SnO2:F/β-Ga2O3 thin-film photodetectors are promising candidates for UVC detection and can be effectively utilized in environmental monitoring applications, such as ozone hole observation.
Highlights
● FTO/β-Ga2O3photodetectors were fabricated via spray pyrolysis and optimized at 0.2 M Ga2O3.
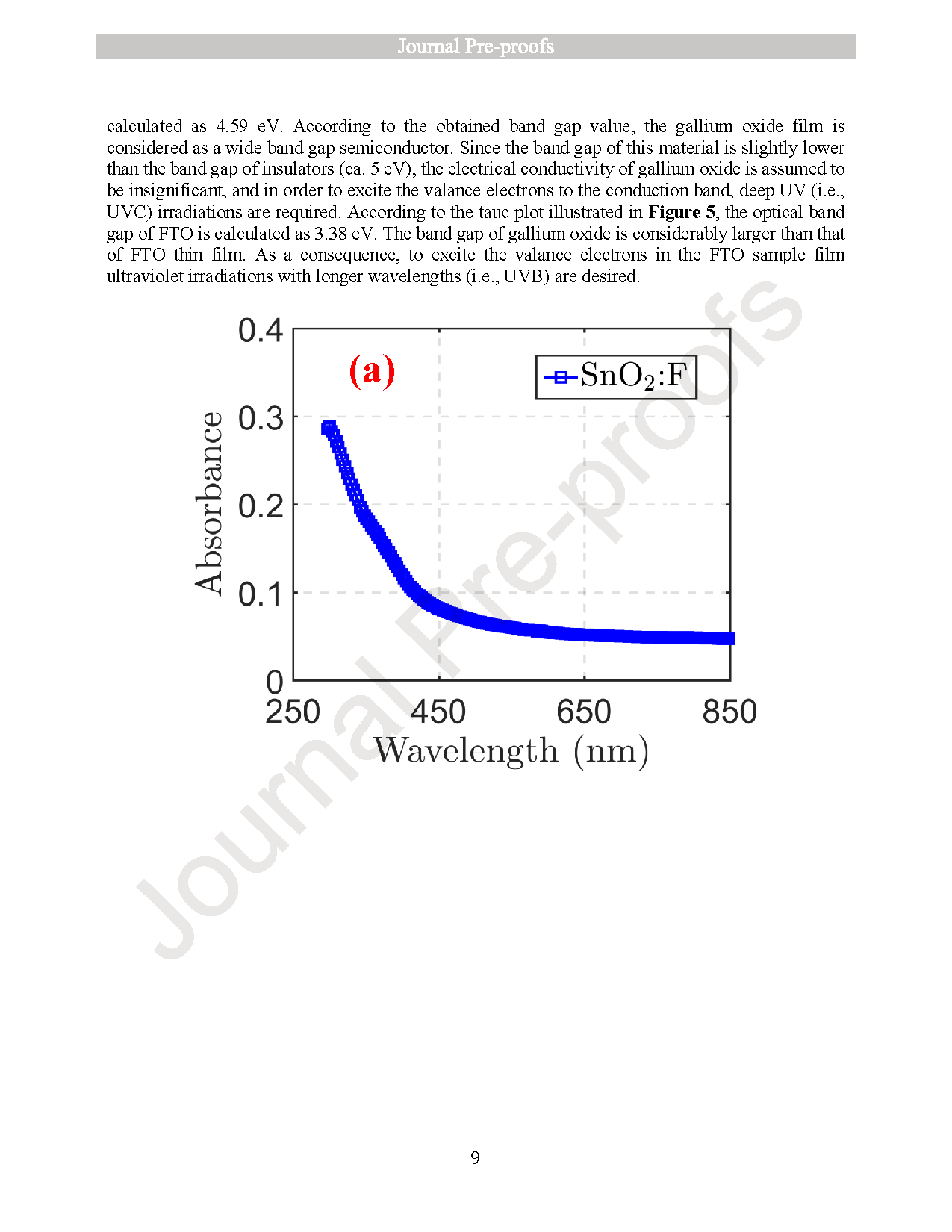
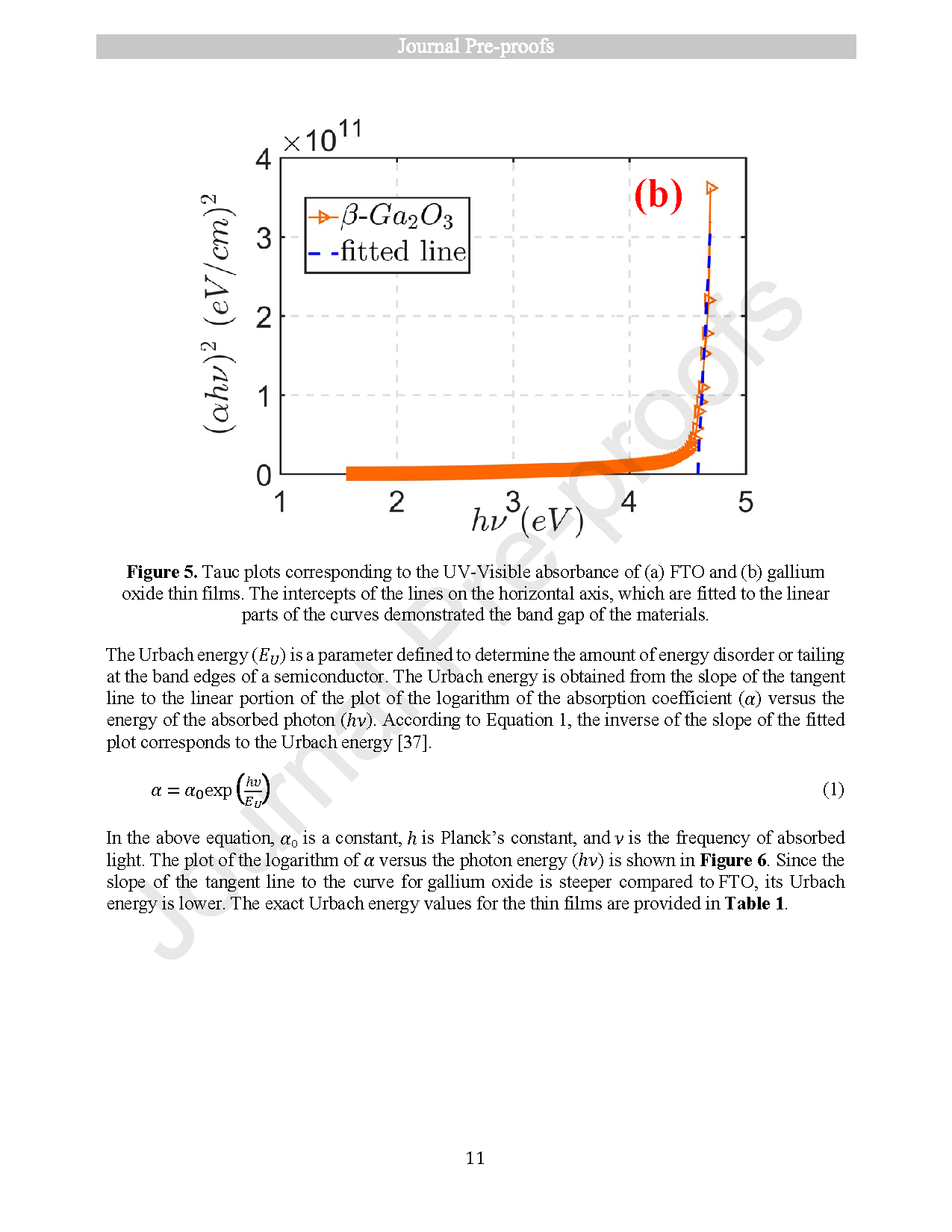
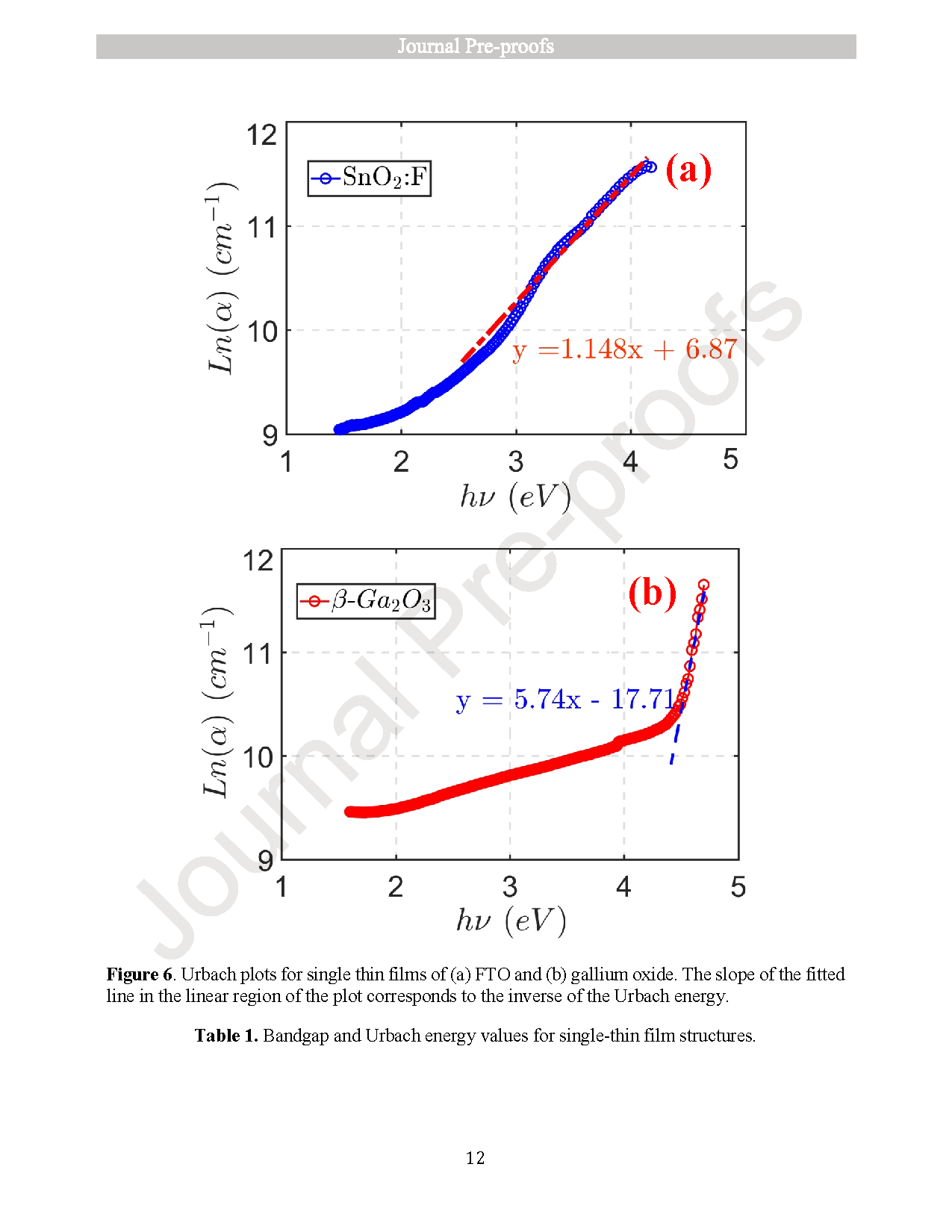
● Films showed band gaps of 4.59 eV (β-Ga2O3) and 3.38 eV (FTO), with superior FTO crystallinity.
● The optimized device achieved 47.72 mA/W responsivity and 3.34 × 108 Jones detectivity for UVC monitoring.
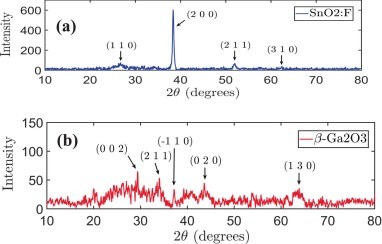
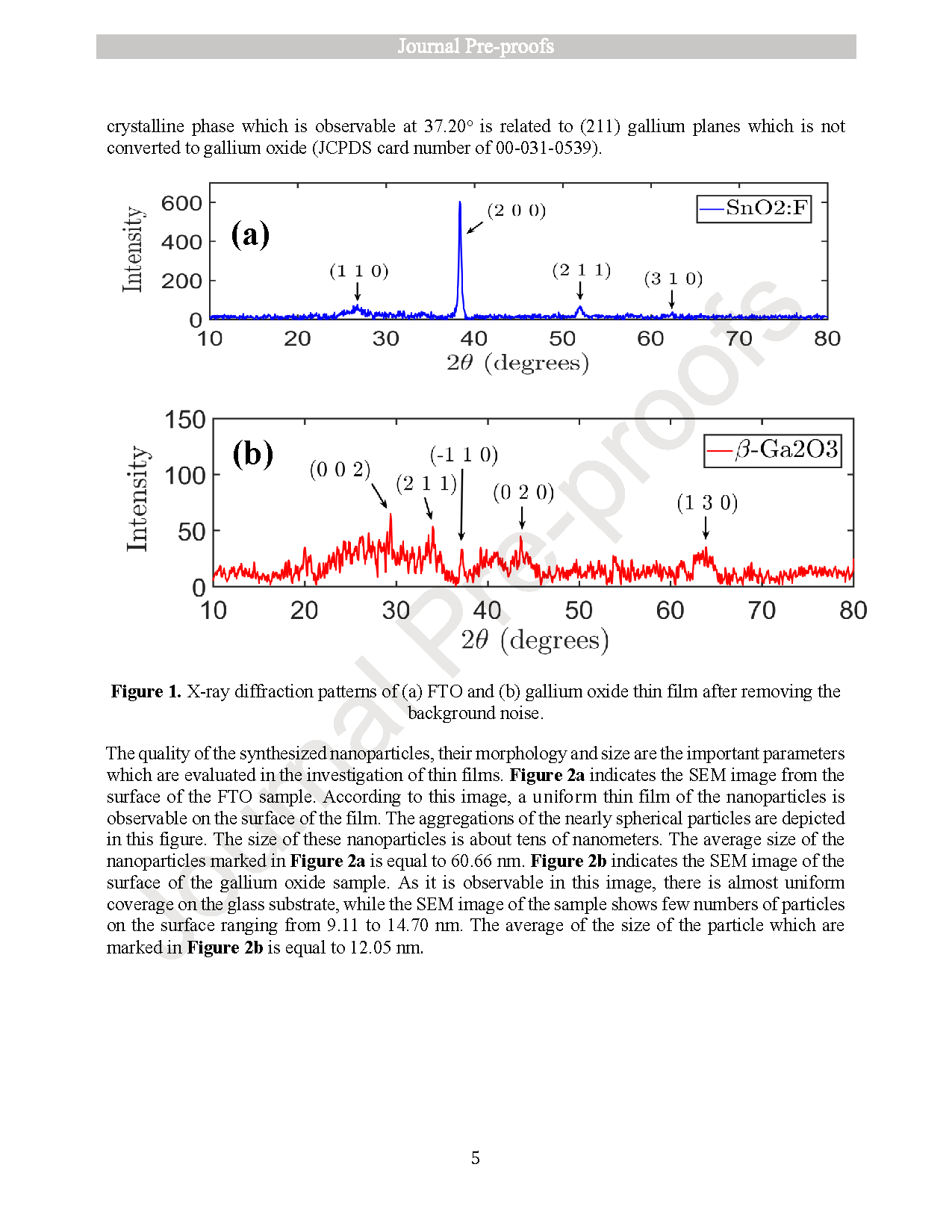
Fig. 1. X-ray diffraction patterns of (a) FTO and (b) gallium oxide thin film after removing the background noise.
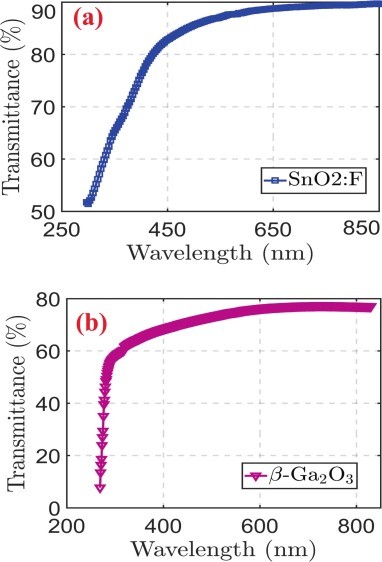
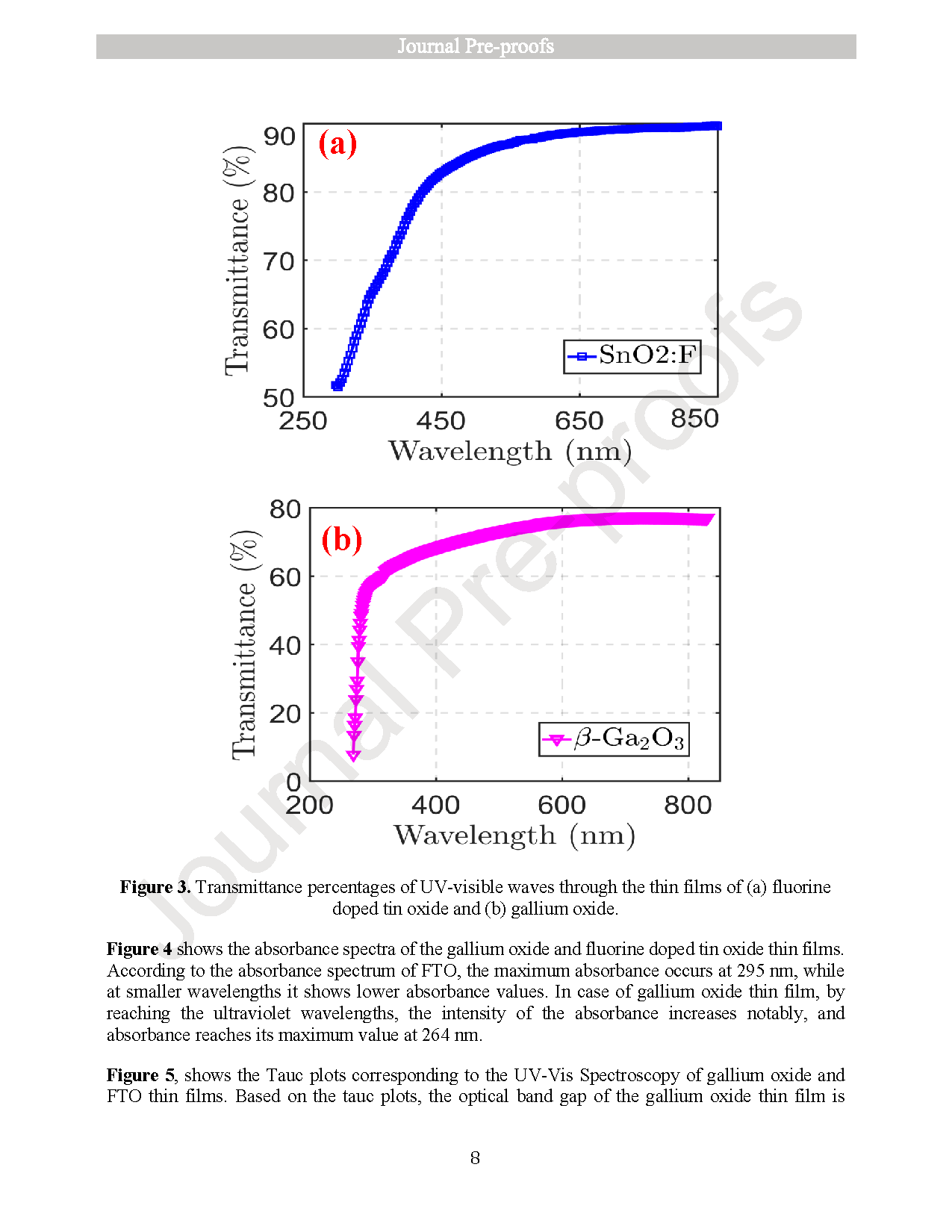
Fig. 2. Transmittance percentages of UV–visible waves through the thin films of (a) fluorine doped tin oxide and (b) gallium oxide.
DOI:
doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2025.108375