【Member Papers】Bias-tuned Selective Spectral Response high-performance Ga₂O₃/GaN Heterojunction Ultraviolet Photodetector
日期:2025-06-23阅读:320
Researchers from the Northeast Normal University have published a dissertation titled "Bias-tuned Selective Spectral Response high-performance Ga2O3/GaN Heterojunction Ultraviolet Photodetector" in IEEE Electron Device Letters.
Project Support
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO. 62274027 and 62404039), the Open Research Fund of Song Shan Lake Materials Laboratory (2023SLABFK03), 111 Center (B25030) and the Funding from Jilin Province (NO. 20220502002 GH), the Postdoctoral Fellowship Program of CPSF (GZC20230416), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2412024QD010).
Background
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation, although constituting only a small fraction of solar radiation, exerts profound impacts on human life. UV radiation not only facilitates the synthesis of vitamin D and inhibits bacterial growth but also induces several beneficial biological effects. However, excessive UV exposure poses significant health risks, particularly in the UVC range (200-280 nm), known as the solar-blind deep ultraviolet (DUV) region. When the radiation energy exceeds 102 mJ/cm2, it can cause severe adverse effects on human health. Consequently, photodetectors (PDs) for solar-blind radiation have become a focal point of research. Due to strong atmospheric scattering, UVC radiation effectively eliminates interference from solar radiation, making it suitable for applications such as missile warning systems, fire alarms, environmental monitoring, and air-to-air communication.
Abstract
β-Ga2O3 films were successfully fabricated using the GaN thermal oxidation method, and Ga2O3/GaN heterojunction ultraviolet photodetectors were constructed with varying electrode parameters, including length, width, and electrode spacing. Under optimized electrode parameters, the detector demonstrates an exceptionally low dark current, with a value of just 63.2 fA at a 10V bias. Under 33 μW/cm2 ultraviolet light illumination, the detector demonstrates a high light-to-dark current ratio exceeding 106. By adjusting the thickness of the β-Ga2O3 light-absorbing layer to enhance ultraviolet light absorption and reduce carrier recombination, the detector achieves a responsivity of up to 3061 A/W and a detectivity exceeding 1015 Jones. Additionally, by tuning the applied bias, the detector enables adjustable control over both the solar-blind ultraviolet single-band and solar-blind-near ultraviolet dual-band response spectra. These research findings provide important theoretical support and experimental basis for the optimized design and application of high-performance ultraviolet photodetectors.
Conclusion
In summary, this work demonstrates a Ga2O3/GaN heterojunction ultraviolet photodetector (PD) fabricated via thermal oxidation. The detector exhibits exceptional performance, with a light-to-dark current ratio exceeding 106, an ultra-high responsivity of 3061 A/W, and a detectivity greater than 1015 Jones. Moreover, by tuning the applied bias, the device allows for flexible control over both the solar-blind ultraviolet single-band and solar-blind-near-ultraviolet dual-band response spectra.
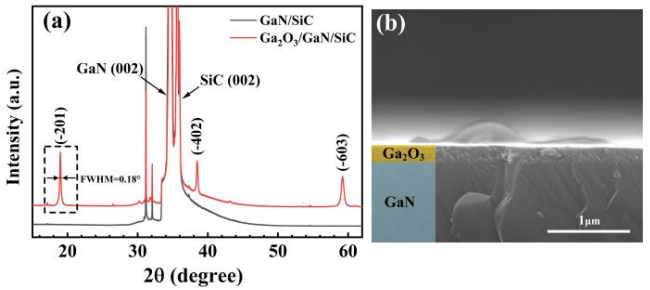
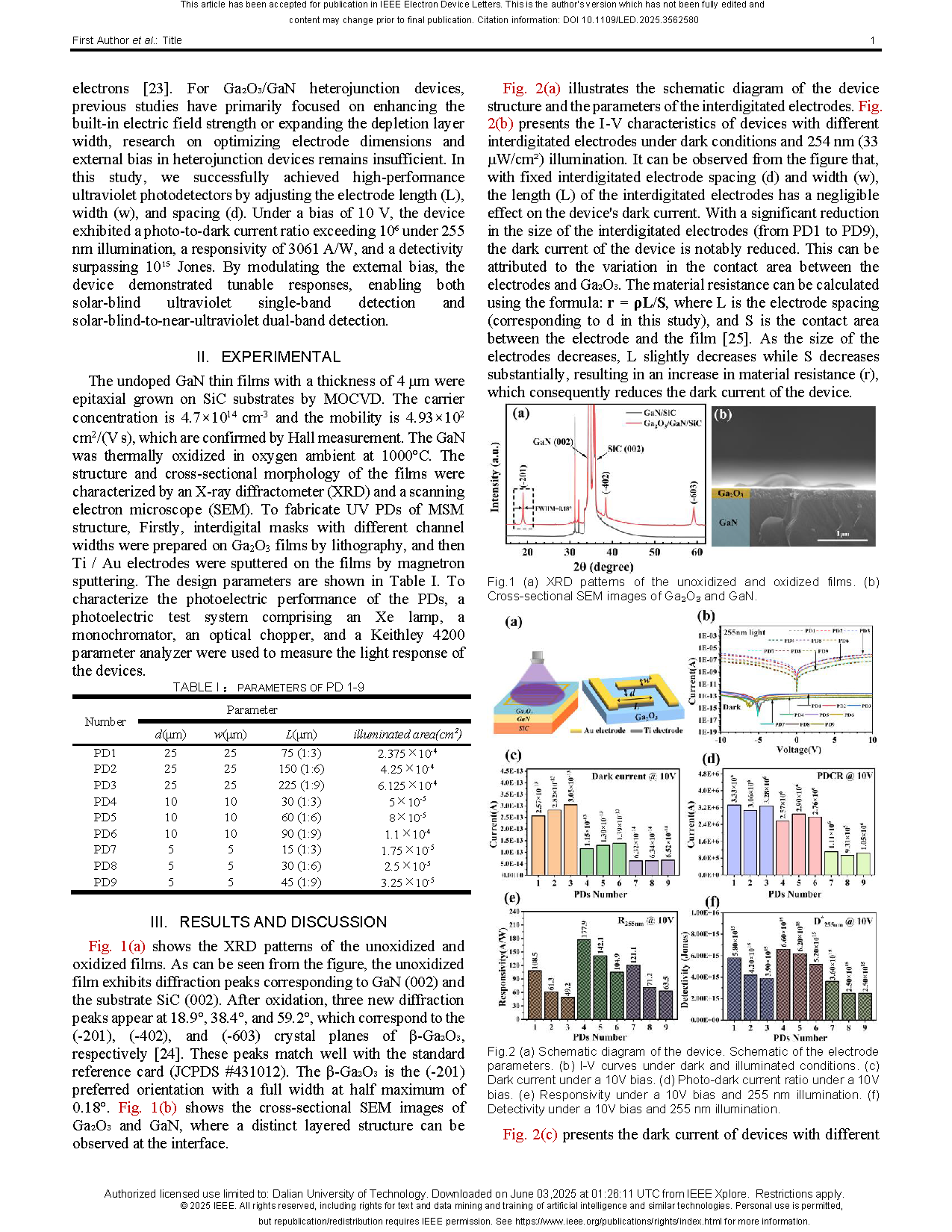
Fig.1 (a) XRD patterns of the unoxidized and oxidized films. (b) Cross-sectional SEM images of Ga2O3 and GaN.
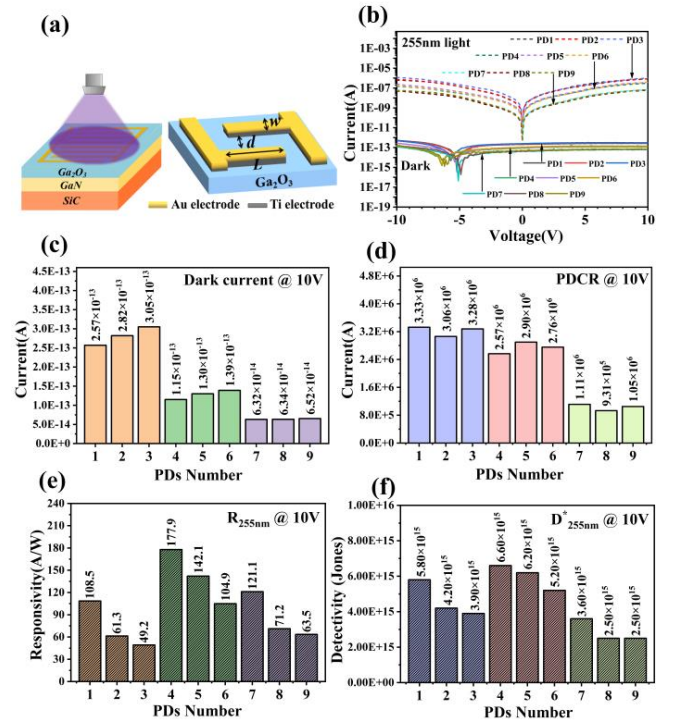
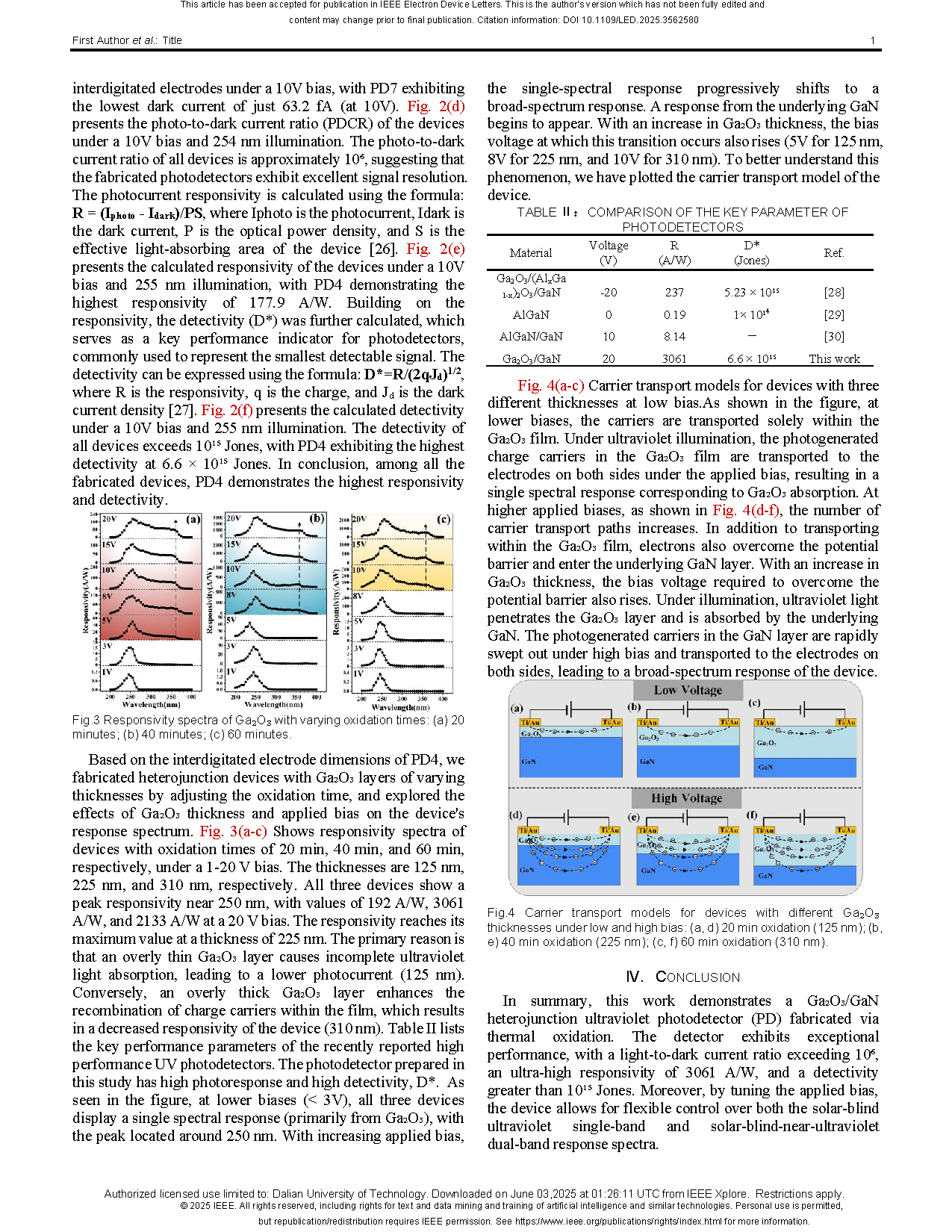
Fig.2 (a) Schematic diagram of the device. Schematic of the electrode parameters. (b) I-V curves under dark and illuminated conditions. (c) Dark current under a 10V bias. (d) Photo-dark current ratio under a 10V bias. (e) Responsivity under a 10V bias and 255 nm illumination. (f) Detectivity under a 10V bias and 255 nm illumination.
DOI:
doi.org/10.1109/LED.2025.3562580