【Domestic Papers】Transition-Rule Defined Polarization Detection of β-Ga₂O₃ for Wavelength-Dependent Sensing of Amino Acid
日期:2025-06-23阅读:304
Researchers from Songshan Lake Materials Laboratory and Shandong University of Technology have published a paper titled "Transition-Rule Defined Polarization Detection of β-Ga2O3 for Wavelength-Dependent Sensing of Amino Acid" in Laser & Photonics Reviews.
Project Support
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 12174275, 62174113, 12204471, and 12474073) and the Youth Innovation Team of Colleges and Universities in Shandong Province (Grant No. 2022KJ223).
Background
Polarization photodetectors (PPDs) have extensive applications in medical imaging, optical communication stress imaging and defogging imaging since the polarization state carries the information of surface roughness, texture pattern, and physical and chemical properties which are unattainable in conventional intensity-based PDs. Furthermore, the integration of PPDs with light-triggered color-switching materials and humidity-responsive spin-state materials could enable multi-modal optical sensing systems for secure communication and adaptive environmental monitoring. Integration with wire grids has achieved great success in visible infrared and Terahertz bands, where polarization cameras are now commercially available globally. However, the development of wire-grid deep-ultraviolet (DUV) PPDs is encountering tremendous obstacles due to the difficulties in preparing high-density nanoscale wire grids on a large scale. It is well known that the wire-grid period must be less than the incident wavelength to ensure a high extinction ratio according to the effective medium theory. β-Ga2O3 has received significant research attention due to its ultrawide bandgap, high photoresponsivity (R), and anisotropic optical properties in this special band. Compared to integrating metal-grid structure with periods of 100 and 167 nm using a sophisticated focused ion beam process, utilization of the low-symmetric nature of β-Ga2O3 would be more appealing for the advance of DUV PPDs.
Abstract
Selective electron transitions are critical for polarization detection due to the high sensitivity of optoelectronic conversion to symmetry properties. This work proposes a transition-rule-defined wavelength-dependent polarization detector using low-symmetry β-Ga2O3. Density functional theory calculation is applied to predict the dependence of photoresponse bands on polarization angles. A combination of angle-resolved polarization Raman spectroscopy and polarized transmittance spectra is utilized to corroborate the anisotropic optical properties of β-Ga2O3. Intriguingly, a notable proportional inversion of the polarization ratio (PR) emerges at 245 nm when altering the detection wavelength of the β-Ga2O3 photodetector (PD). Specifically, the photoresponse contrast between E//b and E//c directions, termed responsivity PR, can be boosted from 75 at 254 to 462 at 263 nm, while the minimum reaches 1/388 at 231 nm. The unique phenomenon of wavelength-dependent polarization detection in β-Ga2O3 PD well coincides with the density functional theory calculations concerning the selective transition of photoelectrons from split valence bands to the conduction band minimum. Finally, the new transition-rule-defined deep-ultraviolet polarization detector is leveraged to discriminate amino acids. This work demonstrates the remarkable meaning of a delicate control of the selective electron transitions in β-Ga2O3 polarization PDs for amino acid sensing with high sensitivity and specificity.
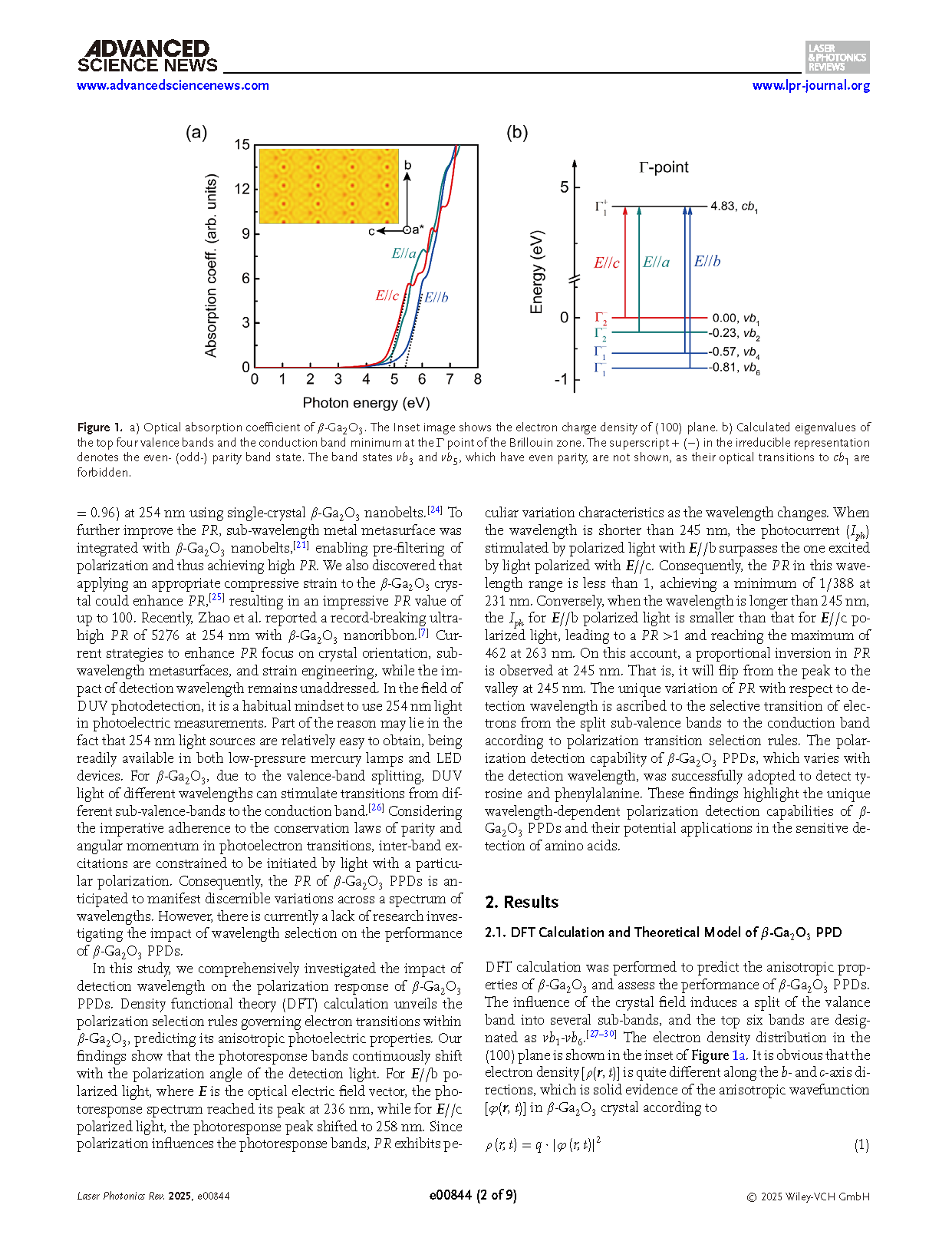
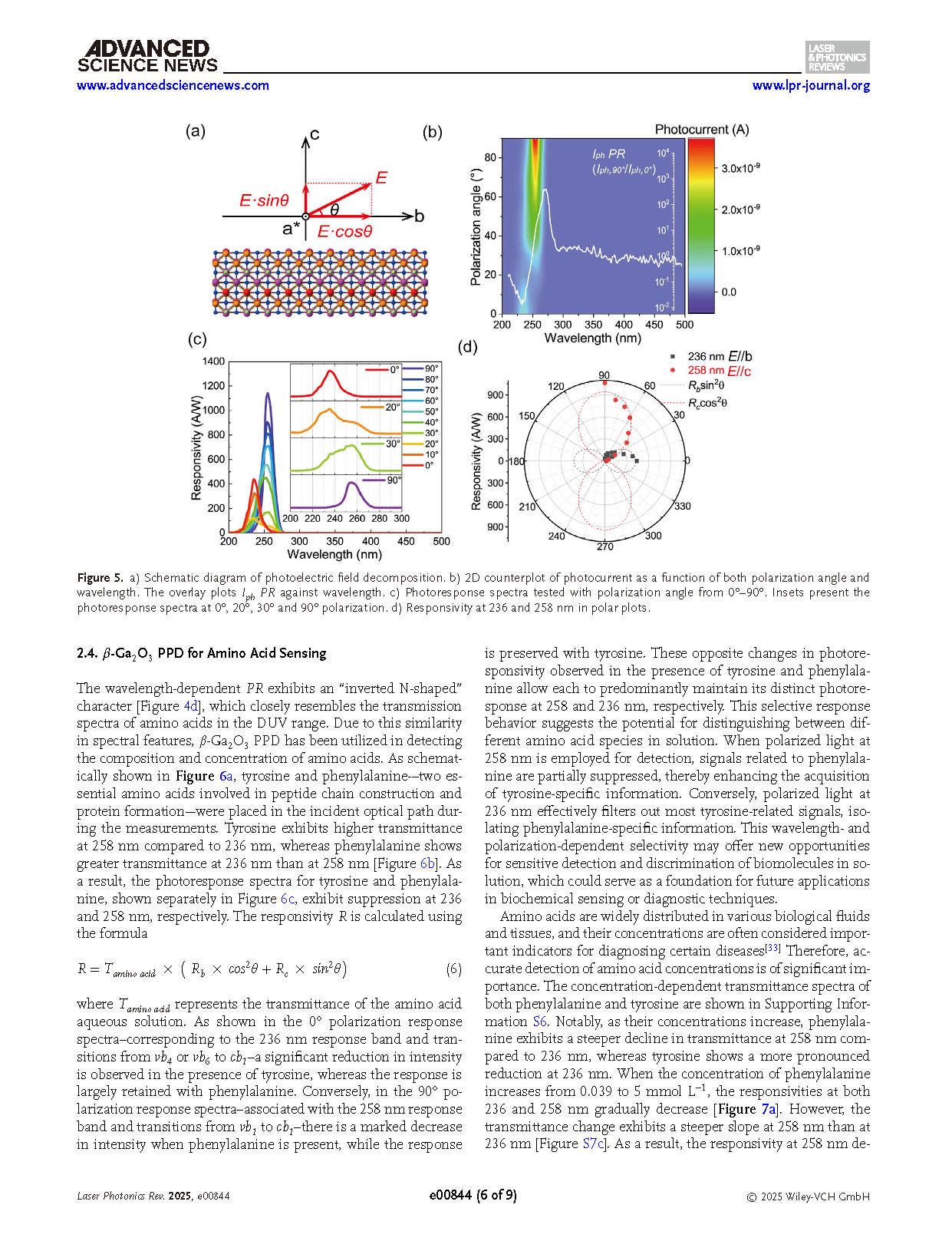
Figure 1. a) Optical absorption coefficient of β-Ga2O3. The Inset image shows the electron charge density of (100) plane. b) Calculated eigenvalues of the top four valence bands and the conduction band minimum at the 「 point of the Brillouin zone. The superscript + (−) in the irreducible representation denotes the even- (odd-) parity band state. The band states vb3 and vb5, which have even parity, are not shown, as their optical transitions to cb1 are forbidden.
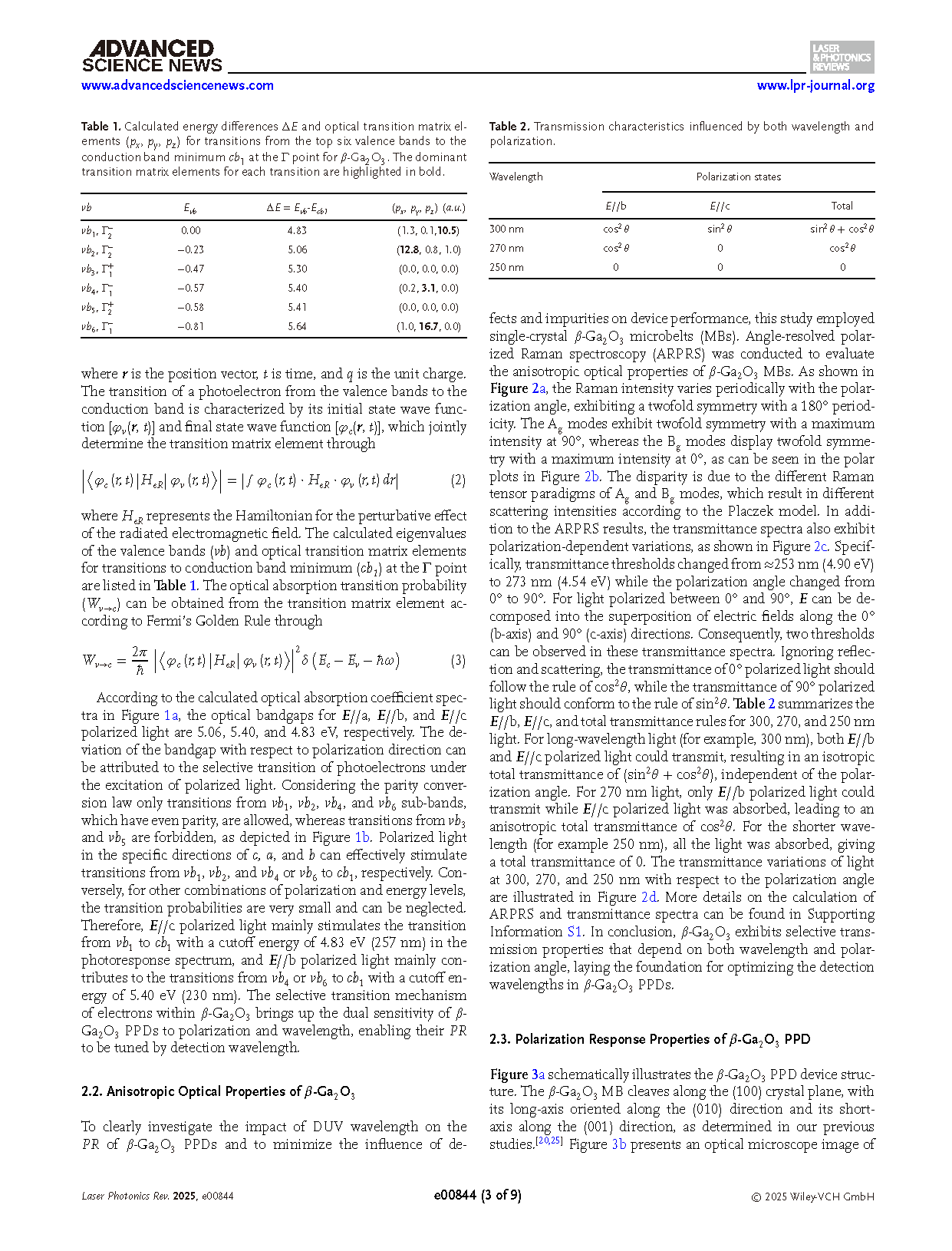
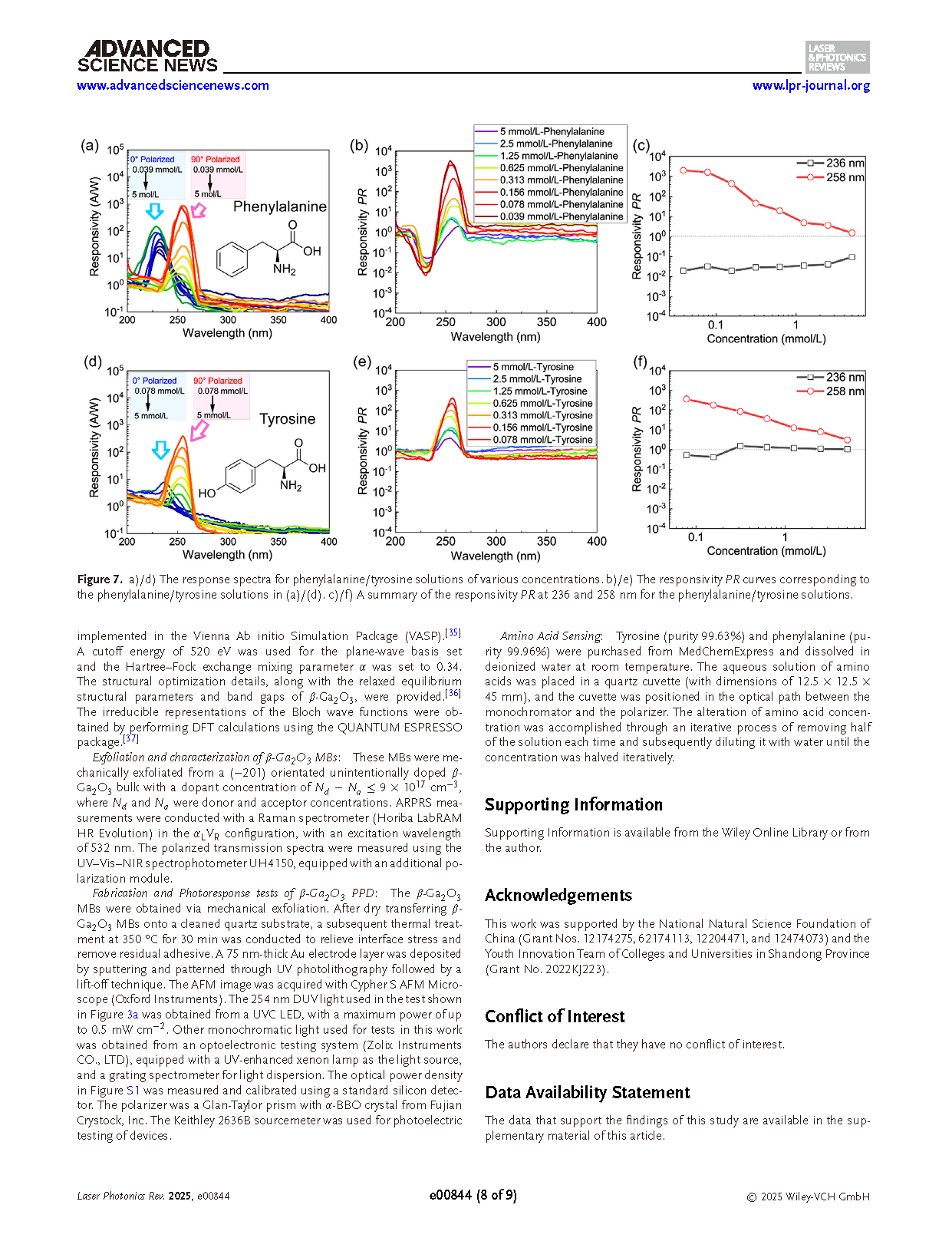
Figure 2. a) ARPRS results of β-Ga2O3 MBs. b) Polar plots of A5 g and B2 g Raman modes, which show orthogonal periodicity. c) Transmittance spectra with polarization angle ranging from 0° to 90°. d) Polar plots of transmittances at 300, 270, and 250 nm wavelength with respect to polarization angle. C1, C2, C3, and C4 are four fitting constants.
DOI:
doi.org/10.1002/lpor.202500844