
【Device Papers】Achieving Face-Selective Ohmic Contact to β-Ga₂O₃ via Anisotropic Trench Structure
日期:2025-09-29阅读:72
Researchers from the Seoul National University have published a dissertation titled "Achieving Face-Selective Ohmic Contact to β-Ga2O3 via Anisotropic Trench Structure" in ACS Applied Electronic Materials.
Abstract
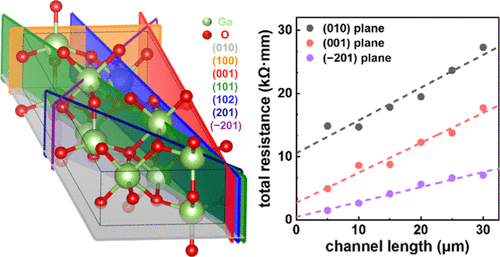
Achieving low contact resistance is crucial for fabricating high-performance electronic and optoelectronic devices. As beta-gallium oxide (β-Ga2O3) with a low-symmetry monoclinic structure exhibits anisotropic electronic properties, we investigated the anisotropic contact resistance of β-Ga2O3 by fabricating trench contact structures on six distinct crystallographic planes ((001), (100), (101), (102), (201), and (−201)) using photo-enhanced metal-assisted chemical etching on undoped (010)-oriented substrates. Trench contact structures enable contacts on distinct crystallographic planes, overcoming the restriction of contact formation to the grown surface. Transfer length method analysis revealed that trench contacts on the (−201) plane yielded the lowest contact resistance (0.23 kΩ·mm). The low atomic density and surface energy enhanced carrier injection at the interface owing to the lower phonon density and formation of a thinner Ti–TiOx interfacial layer, respectively. Asymmetric self-powered ultraviolet–C photodetectors incorporating (−201) trench contacts exhibited superior optoelectronic performance, including a 3-fold increase in responsivity (13.17 mA·W–1) with enhanced photo-to-dark current ratio (1.38 × 104%), compared with that of surface-contacted devices (4.38 mA·W–1, 7.57 × 103%). This work highlights the importance of anisotropic properties in contact engineering and provides a pathway for optimizing β-Ga2O3 devices for next-generation power and photodetection technologies.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaelm.5c01474


