
【Epitaxy Papers】Trigonal pseudomorphism of κ-Ga₂O₃ grown on c-sapphire by HVPE
日期:2025-08-11阅读:102
Researchers from the St. Petersburg State University have published a dissertation titled "Trigonal pseudomorphism of κ-Ga2O3 grown on c-sapphire by HVPE" in Journal of Materials Science.
Abstract
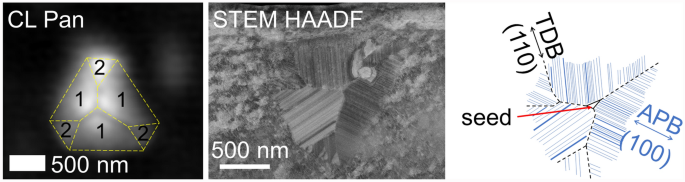
A thick κ-Ga2O3 layer grown by halide vapor phase epitaxy on the smooth sapphire substrate was used for the study of the recombination and structural properties of the gallium oxide κ-phase and its 2D defects. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) revealed two distinct regions on the sample’s surface: flat areas and trigonal-like facets. Cathodoluminescence (CL) imaging revealed that facets exhibit enhanced bright contrast together with small irregular square-like shapes in the flat areas. CL spectra demonstrated noticeable differences in their shapes between flat areas and the facets: The characteristic for κ-Ga2O3 ~ 2.95 eV peak was significantly reduced for the flat part of the layer. Analysis of the structure via transmission electron microscopy (TEM) in a plan-view lamella showed that facets on the surface correspond to relatively large κ-Ga2O3 domains organized in a pseudotrigonal manner. This phenomenon should be considered as a fully-fledged pseudomorphism of κ-Ga2O3 repeating symmetry of the etched sapphire morphology. Domains are divided by the twin domain boundaries (TDBs) and have dense regular arrays of the parallel antiphase boundaries (APBs) inside them. TEM analysis of the flat areas revealed a large number of the unequally sized smaller domains containing only some separate APBs. This structure results in both a significantly lower density of APBs and a higher one of the TDBs in flat areas than in facets. Thus, it is proposed that arrays of electrically active TDBs partially quench the ~ 2.95 eV band and lead to the electrically isolating nature of the sample in lateral directions.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-025-11160-6


